You encounter four main types of gears in machinery: spur gear, helical gear, bevel gear, and worm gear. Each gear type delivers specific advantages for different mechanical needs. The table below highlights how these types of gears serve modern industries:
| Gear Type | Common Applications |
|---|---|
| Spur Gears | Power transmission across many industries |
| Helical Gears | Smoother operation, higher load capacities |
| Bevel Gears | Direction change in differential drives |
| Worm Gears | High reduction ratios for elevators and conveyors |
Types of Gears in Machinery
Spur Gear
You will find the spur gear as the most basic and widely used among all types of gears. This gear has straight teeth that run parallel to the shaft. The design makes it easy to manufacture and maintain. The spur gear operates by meshing its teeth with another gear on a parallel shaft, which allows for efficient power transmission in mechanical systems.
Tip: Spur gears offer high mechanical efficiency, reaching up to 99% in ideal conditions.
Here is a table that summarizes the main aspects of the spur gear:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Spur gears are cylindrical gears with straight teeth cut parallel to their rotational axis. |
| Tooth Design | The straight-tooth design allows for rolling contact, enhancing mechanical efficiency up to 99%. |
| Noise Generation | Simultaneous contact across the tooth width can lead to noise at high speeds, but lubrication helps. |
| Efficiency | High mechanical efficiency, suitable for low to medium speed applications. |
You will notice several advantages and disadvantages when using this gear type:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simple Design and Easy Manufacture | Noise and Vibration |
| High Transmission Efficiency | Limited Shaft Arrangement |
| Good Load Capacity | Wear Under High Speeds |
| No Axial Thrust | Stress on Teeth |
| Reliable and Precise | Less Smooth Transmission Compared to Helical Gears |
| Easy Maintenance |
You can find spur gears in many types of machinery, including:
●Transmissions
●Conveyor systems
●Speed reducers
●Engines and mechanical transportation systems
●Gear pumps and motors
●Machining tools
The spur gear remains a top choice for gear systems that require reliability, easy maintenance, and high efficiency. However, you should consider the noise and vibration issues, especially at higher speeds.
Helical Gear
The helical gear stands out among the types of gears for its angled teeth. These teeth engage gradually, which results in smoother and quieter operation compared to the spur gear. You will see this gear used in applications where noise reduction and smooth power transmission are important.
●The gradual meshing of helical gear teeth facilitates quieter power transmission.
●The angled design allows for longer contact time, reducing vibrations and noise.
●Helical gears provide smoother operation, especially at high speeds.
Here is a table that highlights the main features and limitations of the helical gear:
| Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Smooth Operation | Helical gears provide quieter power transmission due to gradual engagement of teeth, reducing noise. |
| Power Transmission Efficiency | They achieve 94%-98% efficiency, especially beneficial for high-speed applications. |
| High Durability | The design allows for even load distribution, reducing wear and prolonging lifespan. |
| Additional Axial Thrust | Helical gears generate axial forces that can impact efficiency and require special bearings. |
| Potential for Power Loss | Increased heat from sliding friction can lead to power loss, especially at low speeds. |
| High Manufacturing Cost | The complex design and need for precision in manufacturing increase costs significantly. |
You will find helical gears in the following types of machinery:
| Machinery Type | Application Description |
|---|---|
| Industrial Chemistry | Used to slow down centrifugal compressors and turbines, aligning speeds with motors. |
| Automotive Sector | Preferred for transmissions due to greater durability and ability to handle heavy loads. |
| High-Speed Machinery | Recommended for machinery requiring high rotational speeds and continuous operation. |
The helical gear offers clear advantages in terms of noise reduction and durability. However, you must consider the disadvantages, such as the need for special bearings and higher manufacturing costs.
Bevel Gear
The bevel gear plays a unique role in gear systems by changing the direction of power transmission between intersecting shafts. You will see this gear used when you need to transfer motion at an angle, often at 90 degrees. The teeth of the bevel gear are shaped along a conical surface, which allows for efficient angular transmission.
Bevel gears are specifically designed to transmit mechanical energy between intersecting shafts, often at right angles, thereby changing the axis of rotation. This flexibility makes them essential in many mechanical systems.
Here is a table that outlines the advantages and disadvantages of the bevel gear:
| Advantages of Bevel Gear | Disadvantages of Bevel Gear |
|---|---|
| Flexible Operation Angle | Precise Installation Required |
| Mechanical Advantage | High Forces on Bearings |
| Compact Design | Limited Gear Ratio |
| Smooth and Efficient Transmission | Complex Manufacturing |
| High Load Capacity | Noise Concerns |
| Versatility in Gear Types | Sensitivity to Misalignment |
| Durability | Maintenance Requirements |
| Adjustable Speed and Torque Ratios | Specific Gear Pairing |
You will encounter bevel gears in these applications:
●Automotive industry: Used in front and rear axle assemblies for varying wheel speeds.
●Heavy-duty equipment: Commonly used for propulsion or running auxiliary units.
●Aviation: Found in helicopter rotors and airplane accessory gearbox drives.
●Industrial equipment: Utilized in speed reducers and cooling tower fans.
The bevel gear provides versatility and efficiency in changing motion direction. You should pay attention to installation precision and maintenance requirements due to the gear’s sensitivity to misalignment.
Worm Gear
The worm gear stands out among the types of gears for its ability to transmit power between non-parallel shafts and deliver high torque reduction. The worm gear consists of a threaded cylindrical gear (the worm) that meshes with a larger gear (the worm wheel). This arrangement allows for significant speed reduction and high torque output in a compact design.
| Component | Description | Functionality |
|---|---|---|
| Worm | A threaded cylindrical gear that meshes with the worm wheel. | Engages with the worm gear to transmit power at right angles, allowing for compact design. |
| Worm Wheel | The larger gear that the worm interacts with. | Receives power from the worm, enabling significant speed reduction and high torque transmission. |
| Gear Reduction | Achieved through the worm’s spiral thread engaging with the worm wheel. | Allows for high gear reduction ratios, effective for high torque reduction in limited spaces. |
You will benefit from several advantages and face some disadvantages when using worm gears:
| Advantages | Drawbacks |
|---|---|
| High Torque Output | Efficiency concerns |
| Compact Design | Material and manufacturing requirements |
| Self-Locking Capability | Heat dissipation issues |
| Quiet Operation | N/A |
You will find worm gears in these applications:
●Elevators and lifts: Used for their self-locking feature, ensuring safety in vertical transportation.
●Conveyor systems: Commonly found in conveyor belts to reduce motor speed while increasing torque.
●Automated doors and gates: Their self-locking capacity prevents unwanted movement, ensuring security.
●Mining and excavation equipment: Essential for handling heavy-duty tasks with high torque and low speed.
●Agricultural machinery: Provides high torque at lower speeds for tasks like tilling and harvesting.
●Industrial winches and hoists: Ideal for lifting and dragging heavy loads with high torque output.
●Robotics: Used for precise movement control in robotic arms and joints.
●Electric vehicles: Applied in steering and final drive for reduced speeds and increased torque.
●Power tools: Essential for effective power transmission in tools like drills and saws.
●Wind turbines: Helps control rotation speed from blades to generator.
The worm gear excels in applications that require high torque and compact design. You should consider efficiency and heat dissipation as key disadvantages.
Note: Other gear types, such as rack and pinion gear, internal gear, and rack gear, also play important roles in mechanical systems. Internal gear designs allow for compact arrangements and smooth operation in planetary gear systems. Rack gear and rack and pinion gear convert rotational motion into linear motion, which is essential in steering systems and automation.
By understanding the features, advantages, and disadvantages of each gear type, you can select the best gear for your machinery needs.
Comparing Gear Types: Features and Uses
Key Differences Between Gear Types
You will notice that gears differ in how they transmit power, handle force, and fit into machinery. The table below highlights the main operational differences among the four primary gear types:
| Gear Type | Application Description | Force Interactions | Power Transmission Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|
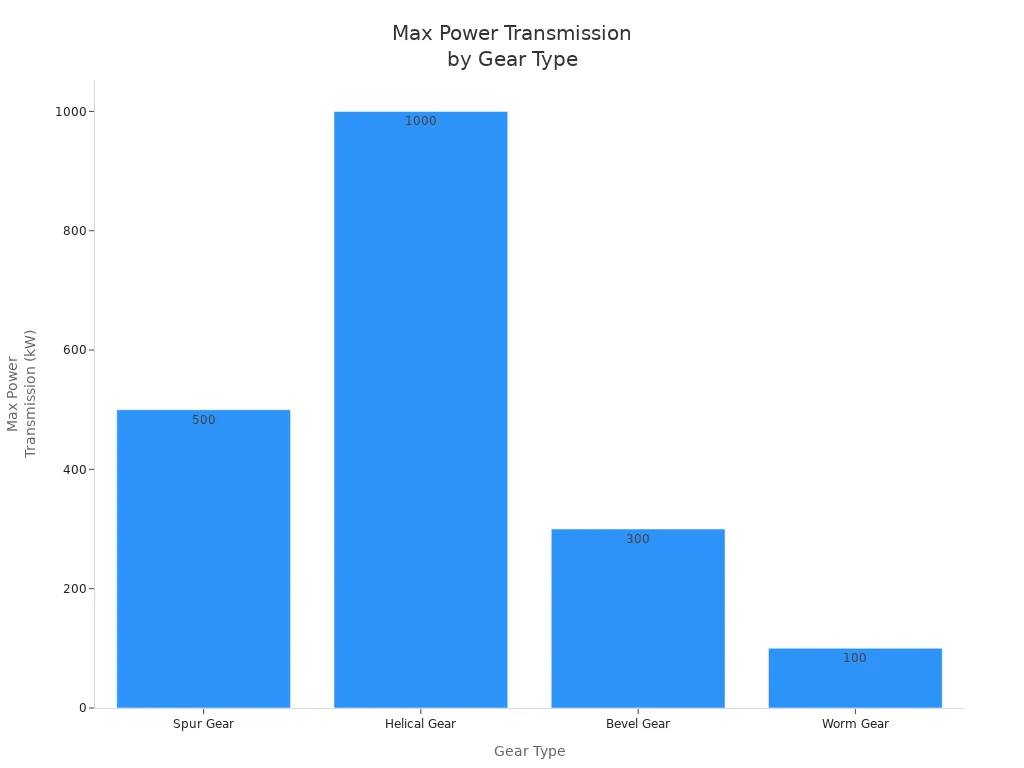
| Spur Gear | Transmits motion and power between two parallel shafts. | Only radial force; no axial thrust. | Up to 500 kW |
| Helical Gear | Works with parallel or non-parallel shafts for smoother operation. | Both radial and axial thrust; gradual tooth engagement. | Up to 1 MW |
| Bevel Gear | Changes direction between intersecting shafts, often at right angles. | Both radial and axial thrust; conical tooth design. | Up to 300 kW or more |
| Worm Gear | Transfers power between non-intersecting, perpendicular shafts. | High friction; both radial and axial thrust; sliding contact. | Up to 100 kW |
You can compare efficiency ratings for these gears in industrial settings:
| Gear Type | Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Spur | Very High (98-99%) |
| Helical | High |
| Bevel | High |
| Worm | Low-Medium |
Noise levels also vary. Worm gears operate at about 65 dB, while helical bevel gears reach 85 dB. You will find that spur gears are less expensive to manufacture than helical gears, which cost 10–15% more but may save energy over time. Maintenance needs differ as well. Spur gears are simple to maintain, while worm gears require special lubricants and more frequent attention.
Choosing the Right Gear
You should consider several factors when selecting gears for your machinery. Start by assessing speed and power requirements. Make sure the gear can handle the load and fits within the available space. Material choice impacts durability and performance. Customizability may be necessary for unique operational needs. Check the bearing system for proper support and alignment. Duty cycle, or how often the gear will run, affects your choice as well.
Tip: Proper gear selection reduces noise, vibration, and heat, which extends machinery lifespan.
You must also evaluate installation space, torque requirements, and environmental conditions. For example, spur gears work well for simple, high-efficiency needs. Helical gears suit high-speed, quiet operations but cost more. Bevel gears excel at changing direction in compact spaces. Worm gears provide high torque and self-locking features but need more maintenance.
| Gear Type | Maintenance Requirement | Special Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Worm Gears | High | Require special lubricants |
| Helical Gears | Moderate | Standard lubrication |
| Spur Gears | Low | Simple and easy to maintain |
| Bevel Gears | Moderate | Precise alignment needed |
When you match the right gear to your application, you improve efficiency, reduce wear, and ensure reliable operation. Always review the specific needs of your machinery before making a final decision.
You have learned about spur, helical, bevel, and worm gears. Each gear type serves a unique purpose in machinery:
| Gear Type | Primary Use Cases |
|---|---|
| Spur | Conveyor systems, automotive machinery |
| Helical | Transmissions, industrial robotics |
| Bevel | Angle drives, marine propulsion |
| Worm | Elevators, steering mechanisms |
Understanding these differences helps you increase torque, control speed, and improve efficiency. Always match your gear choice to your machinery’s requirements for the best results.
FAQ
What gear type should you use for quiet operation?
You should choose helical gears. Their angled teeth reduce noise and vibration, making them ideal for environments where quiet operation matters.
Can you mix different gear types in one machine?
You can combine gear types, but you must ensure compatibility. Always check alignment, load, and speed requirements before mixing gears.
How often should you maintain industrial gears?
●You should inspect gears monthly.
●Lubricate as recommended by the manufacturer.
●Replace worn parts immediately to prevent breakdowns.
Post time: Jan-09-2026