Gear accuracy grades define the tolerances and precision levels of gears based on international standards (ISO, AGMA, DIN, JIS). These grades ensure proper meshing, noise control, and efficiency in gear systems
1. Gear Accuracy Standards
ISO 1328 (Most Common Standard)
Defines 12 accuracy grades (from highest to lowest precision):
Grades 0 to 4 (Ultra-precision, e.g., aerospace, metrology)
Grades 5 to 6 (High precision, e.g., automotive transmissions)
Grades 7 to 8 (General industrial machinery)
Grades 9 to 12 (Low precision, e.g., agricultural equipment)
AGMA 2000 & AGMA 2015 (US Standard)
Uses Q-numbers (Quality Grades):
Q3 to Q15 (Higher Q = better precision)
Q7-Q9: Common for automotive gears
Q10-Q12: High-precision aerospace/military
DIN 3961/3962 (German Standard)
Similar to ISO but with additional tolerance classifications.
JIS B 1702 (Japanese Standard)
Uses Grades 0 to 8 (Grade 0 = highest precision).
2. Key Gear Accuracy Parameters
Accuracy grades are determined by measuring:
1.Tooth Profile Error (Deviation from ideal involute curve)
2.Pitch Error (Variation in tooth spacing)
3.Runout (Eccentricity of gear rotation)
4.Lead Error (Deviation in tooth alignment)
5.Surface Finish (Roughness affects noise & wear)
3. Typical Applications by Accuracy Grade
| ISO Grade | AGMA Q-Grade | Typical Applications |
| Grade 1-3 | Q13-Q15 | Ultra-precision (Optics, aerospace, metrology) |
| Grade 4-5 | Q10-Q12 | High-end automotive, robotics, turbines |
| Grade 6-7 | Q7-Q9 | General machinery, industrial gearboxes |
| Grade 8-9 | Q5-Q6 | Agricultural, construction equipment |
| Grade 10-12 | Q3-Q4 | Low-cost, non-critical applications |
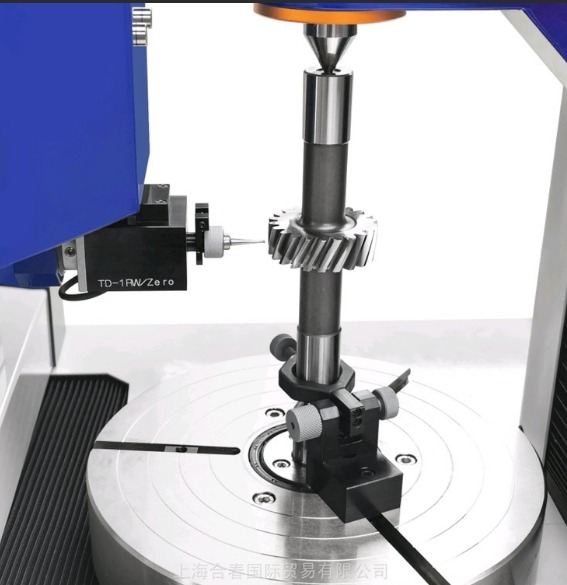
4. How Gear Accuracy is Measured?
Gear Testers (e.g., Gleason GMS Series, Klingelnberg P-series)
CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine)
Laser Scanning & Profile Projectors
Gleason’s Gear Inspection Systems
GMS 450/650: For high-precision spiral bevel & hypoid gears
300GMS: For cylindrical gear inspection
5. Choosing the Right Accuracy Grade
Higher Grade = Smoother operation, less noise, longer life (but more expensive).
Lower Grade = Cost-effective but may have vibration & wear issues.
Example Selection:
Automotive Transmission: ISO 6-7 (AGMA Q8-Q9)
Helicopter Gears: ISO 4-5 (AGMA Q11-Q12)
Conveyor Systems: ISO 8-9

Post time: Aug-01-2025