Definition and Formula
The gear module is a fundamental parameter in gear design that defines the size of the gear teeth. It is calculated as the ratio of the circular pitch (the distance between corresponding points on adjacent teeth along the pitch circle) to the mathematical constant π (pi). The module is typically expressed in millimeters (mm).

Where:
● m = gear module
● cp = circular pitch
Key Functions of the Gear Module
1.Standardization:
The module standardizes gear dimensions, enabling compatibility, interchangeability, and ease of mass production.
2.Strength Determination:
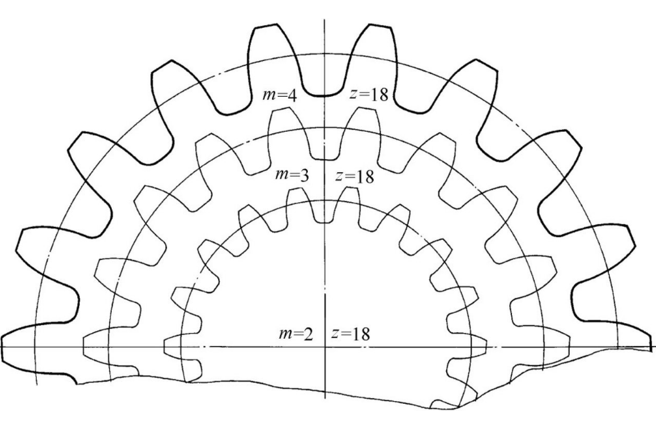
The module directly affects the thickness and strength of gear teeth. A larger module results in stronger teeth, capable of handling higher loads.
3.Dimensional Influence:
It influences critical gear dimensions such as the outside diameter, tooth height, and root diameter.
Module Selection Criteria
● Load Requirements:
Higher mechanical loads require a larger module to ensure adequate strength and durability.
● Speed Considerations:
For high-speed applications, a smaller module is preferred to minimize inertial forces and reduce noise.
● Space Constraints:
● In compact or space-limited designs, a smaller module allows for reduced overall gear size while maintaining functionality.
Standard Module Sizes
Common standardized module values include:
0.5, 0.8, 1, 1.25, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12, 16, 20, 25, 32, 40, 50, etc.
Example Calculation
If the circular pitch cpcpcp is 6.28 mm, the gear module mmm is calculated as:
m=6.28π≈2 mmm = \frac{6.28}{\pi} \approx 2\ \text{mm}m=π6.28≈2 mm
Summary
The gear module is a crucial design parameter that affects the size, strength, and performance of a gear. Selecting the appropriate module ensures optimal functionality, reliability, and compatibility based on specific application demands, including load, speed, and space limitations.
Post time: May-09-2025