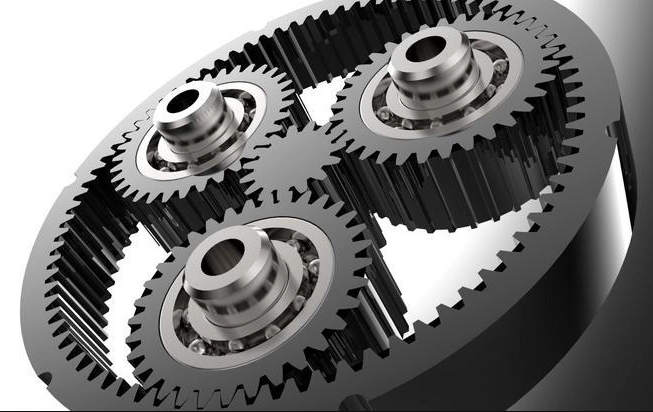
A planetary gear (also known as an epicyclic gear) is a gear system consisting of one or more outer gears (planet gears) revolving around a central (sun) gear, all held within a ring gear (annulus). This compact and efficient design is widely used in automotive transmissions, industrial machinery, and robotics due to its high torque density and versatility in speed reduction/amplification.
Components of a Planetary Gear System
Sun Gear – The central gear, usually the input.
Planet Gears – Multiple gears (typically 3-4) that mesh with the sun gear and rotate around it.
Ring Gear (Annulus) – The outer gear with inward-facing teeth that mesh with the planet gears.
Carrier – Holds the planet gears and determines their rotation.
How It Works
Planetary gears can operate in different modes depending on which component is fixed, driven, or allowed to rotate:
Fixed Component Input Output Gear Ratio Application Example
Sun Gear Carrier Ring Gear High reduction Wind turbines
Ring Gear Sun Gear Carrier Speed increase Automotive automatic transmissions
Carrier Sun Gear Ring Gear Reverse output Differential drives
Speed Reduction: If the ring gear is fixed and the sun gear is driven, the carrier rotates slower (high torque).
Speed Increase: If the carrier is fixed and the sun gear is driven, the ring gear rotates faster.
Reverse Rotation: If two components are locked together, the system acts as a direct drive.
Advantages of Planetary Gears
✔ High Power Density – Distributes load across multiple planet gears.
✔ Compact & Balanced – Central symmetry reduces vibration.
✔ Multiple Speed Ratios – Different configurations allow varied outputs.
✔ Efficient Power Transfer – Minimal energy loss due to shared load distribution.
Common Applications
Automotive Transmissions (Automatic & Hybrid Vehicles)
Industrial Gearboxes (High-torque machinery)
Robotics & Aerospace (Precision motion control)
Wind Turbines (Speed conversion for generators)
Post time: Aug-29-2025