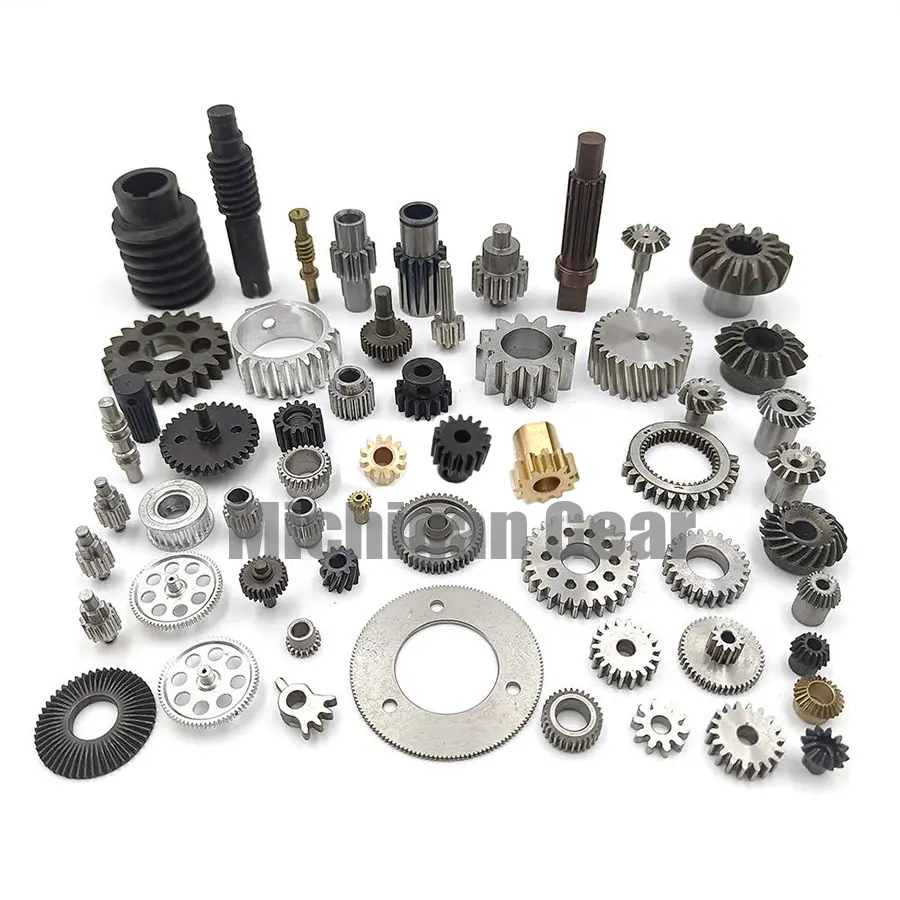
Cylindrical gears transmit mechanical power between parallel shafts using a cylindrical pitch surface. You can distinguish these gears by their tooth orientation and engagement style.
Key Takeaways
● Cylindrical gears are essential for transmitting power between parallel shafts, making them crucial in many mechanical systems.
cylindrical gears features and types
main characteristics
When you examine cylindrical gears, you notice several defining features that set them apart in mechanical systems. These gears have a cylindrical pitch surface, which means the teeth are cut around a cylinder. You typically use them to connect parallel shafts, making them essential in many gear train designs.
● The pitch point divides the line between the centers of two gears. This point determines the gear ratio and influences how smoothly power transfers between gears.
The orientation of the teeth also plays a crucial role in performance. Spur gears have straight teeth, while helical gears feature angled teeth. This difference affects how the gears engage and the amount of noise they produce.Tip: Always consider the shaft arrangement and tooth orientation when selecting a gear for your application. These factors directly impact efficiency, noise, and durability.
spur, helical, and double helical gears
You will encounter three main types of cylindrical gears: spur, helical, and double helical. Each type offers unique advantages and fits specific applications.
| Feature | Spur Gear | Helical Gear | Double Helical Gear |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tooth Orientation | Straight, parallel | Angled to axis | Two sets, opposite angles |
| Engagement | Abrupt, full tooth width | Gradual, starts at one end | Smooth, self-aligning |
| Noise Level | Higher | Lower | Very low |
| Axial Thrust | None | Generated | Eliminated |
| Typical Use | Low-speed, simple drives | High-speed, heavy loads | Large gearboxes, turbines |
Spur gears have straight teeth aligned parallel to the axis of rotation. You often use them in low-speed applications, such as small conveyor systems or basic gear trains, because they can become noisy at higher speeds. Helical gears, with their angled teeth, provide smoother and quieter operation. You will find them in automotive transmissions and industrial robotics, where high speed and load capacity matter. Double helical gears, also known as herringbone gears, combine two sets of helical teeth with opposite angles. This design eliminates axial thrust and provides self-alignment, making them ideal for large-scale gearboxes, power plants, and marine propulsion systems.
Material selection also plays a vital role in gear performance. You can choose from several materials, each with its own benefits and drawbacks:
| Material | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Alloy Steel | High strength, excellent wear resistance | More expensive, requires precise machining |
| Carbon Steel | Cost-effective, easy to machine | Lower wear and corrosion resistance |
| Stainless Steel | Excellent corrosion resistance, stable operation | Higher cost, average strength |
| Cast Iron | Good wear resistance, handles heavy loads | Lower toughness, prone to cracking |
| Engineering Plastics | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good friction | Poor high-temp performance, lower strength |
You should select the material based on your application’s load, environment, and required durability. For example, alloy steel suits high-load gear trains, while engineering plastics work well in lightweight or corrosion-prone environments.
By understanding these features and types, you can make informed decisions when designing or maintaining a gear train. The right choice ensures optimal performance, longevity, and efficiency in your mechanical systems.
how cylindrical gears work
working principle
You use cylindrical gears to transfer motion and force between parallel shafts. When one gear rotates, its teeth mesh with the teeth of another gear, causing the second gear to turn in the opposite direction. The gear ratio depends on the number of teeth on each gear. This ratio controls the speed and torque you get from the gear train. You can achieve precise movement and efficient power transfer because the teeth maintain constant contact. The cylindrical shape ensures smooth engagement and steady force transmission.
advantages and disadvantages
Cylindrical gears offer several benefits for your mechanical systems:
● You get efficient power transmission with minimal energy loss, which boosts machinery performance.
common applications
You find cylindrical gears in many machines that require reliable power transmission. Compressors and power units use these gears because they handle high loads and maintain running accuracy. The design allows for smaller rotor clearances, making assembly easier and improving performance. You also see them in gearboxes, conveyors, and industrial machinery where a precise gear ratio is essential for smooth operation.
cylindrical and bevel gears comparison
key differences
When you compare cylindrical and bevel gears, you see clear differences in how they handle motion and force. The most important distinction lies in the axis arrangement. Cylindrical gears work with parallel shafts, while bevel gears connect shafts that intersect, often at a right angle. This difference shapes their design and the way you use them in a gear train.
| Gear Type | Axis Arrangement |
|---|---|
| Cylindrical Gears | Parallel axes |
| Bevel Gears | Axes intersect at angle |
You use cylindrical gears when you need to transmit power between shafts that run side by side. This setup is common in gear trains for transmissions, conveyor belts, and gear pumps. The gear ratio in these systems stays consistent because the shafts remain parallel. In contrast, bevel gears let you change the direction of motion. You find them in right angle drives, milling machines, and positioning equipment, where the shafts meet at an angle.
● Cylindrical gears provide smooth power transfer in applications that require parallel shaft alignment.
FAQ
What is the main advantage of using helical gears over spur gears?
You get quieter operation and higher load capacity with helical gears. The angled teeth engage gradually, which reduces noise and vibration.
Can you use cylindrical gears for non-parallel shafts?
No, you cannot. Cylindrical gears only work with parallel shafts. For intersecting shafts, you should use bevel gears.
Which material should you choose for high-load applications?
● You should select alloy steel for high-load applications.
Post time: Jan-05-2026